Machine Restart Guideline for Industrial Gearbox
Condition of the oil prior to restarting a gearbox after a prolonged or unplanned stoppage would make the difference between smooth operation and unwanted wear as well as surge in temperature. Here is a list of possible scenarios that can adversely affect performance output of the gear box due to lubricant starvation and remedies to ideally prep the gearbox before restart. Condition of the oil is an indicator of the long-term reliability of the gear box.
Possible affects due to prolonged stoppage
Oil draining off from gear contact zone and non-contact areas, due to gravity. This can result in dry start condition
Chocked filters with contamination and wear particles
Consumption of additive package
Oxidation due to prolonged idle time
Residue and sludge formation due to oxidation
Settlement of wear particles on the bottom of oil sump
Formation of reactive by products which can corrode bearings and gears, due to prolonged idle time.

If Synthetic gear oil is used:
Synthetic oils offer three to five times better resistance to oxidation. Hence check oil for residue / sludge formation / drastic colour change (darkening). If none of the above exists you can continue using the existing oil
Restarting after prolonged stoppage
Check oil filters whether they are loaded with contaminants or wear particles. Clean filters or change them as necessary
Remove 10 % of oil sump quantity from the drain hole to clear contaminants and wear particles settled in the gear box. Top-up with fresh oil quantity equal to that of the drained oil quantity
Check last oil change date. In case of Mineral oil, If the earlier lubrication date was around six to eight months back, followed with stoppage of more than 30 days, change the oil
In case of Synthetic gear oil, If the earlier lubrication date was around 1.5 years back, followed with the stoppage period of more than 30 days, change the oil
If above conditions are not applicable, then check the oil sample for viscosity, viscosity index and TAN number in a lab. If they are within limits continue with existing oil
Pour small quantity of oil manually by opening the top cover of the gear box (Quantity is based on the number of gear reduction stages) until a thin film of oil cover the gears and bearings. This will avoid dry running during start up. Care should be taken to ensure that this additional quantity of oil does not increase the oil sump level beyond the maximum limit
Check oil level in the gear box. It should be around the midpoint between minimum and maximum level. Topup with fresh oil, if necessary
Check formation of residues and smudging of inspection glass and oil level indicator. Clean them accordingly
If gear box has force feed lubrication, check condition of valves, gauges, filters, nozzle and carry out necessary changes accordingly. Pump oil for a few minutes under idle condition before restarting the gear box

Machine Restart Guideline
General guideline to check condition of lubricant (greases and oils) in machines after prolonged stoppage to ensure maximum performance and avoid wear damage
Do not start any bearing in full load and maximum speed condition immediately after extended stoppage period. If possible, run the bearings under no load condition for one hour, before increasing the load and speed in steps
Where ever dynamic or static seals are provided in the equipment, check them for hardening and brittleness. Change the seals if they have become too hard or brittle
Equipments which are prone for mis-alignment as per maintenance records, should be checked for alignment before restarting them
All grease guns and grease pumping equipments need to be recalibrated, before being put to use. Grease in containers to be checked for oil separation and stirred with a clean rod wherever necessary
All oil storage drums should be checked for sedimentation and cleanliness. Thoroughly shake oil drums/ oil cans before taking oil for lubrication
For rust removal of machine parts such as housing, bearings, gears etc, Beruclean 3849 is recommended
The recommendations are based on our books of experience and available knowledge at the time of release. The general guidelines are to check condition of lubricant (greases and oils) in machines due to unplanned stoppage that can be affected due to a combination of known and unknown factors including natural ageing, environmental impact or contamination by external impurities. For further reference and practices specific to the equipment, we suggest you to follow the machine manual or contact the Service team. This information is intended as a guide and does not necessarily represent a marketing specification. To address your concerns, please contact our Engineering Team on +91 80 66900800 / +91 9379917484
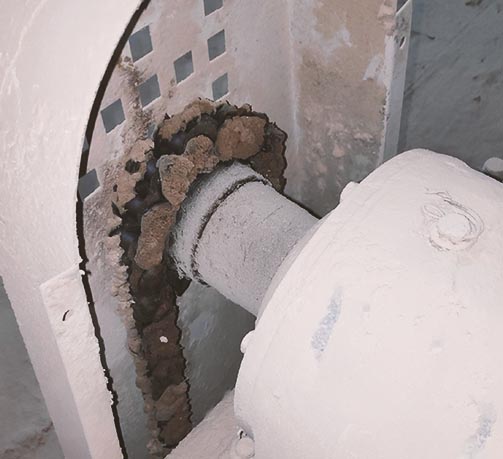

Machine Restart Guideline for Chains
Chain links running dry is sure way to wear, noisy operation and breakdown. Cause for worry if you are restarting chain drives after prolonged downtime. Chain drives are used to transmit force and motion between parallel shafts. Many varieties of chains are in use like heavy duty roller chains, precision roller chains, flat top crate conveyors, duplex or triplex roller chains, inverted tooth or silent chains. While friction characteristics of these types of chains vary depending on construction and mounting position, there are common challenges in ensuring effective lubrication of drive chains. And special care should be taken while restarting chain drives after prolonged stoppage.

Machine Restart Guideline for Bearing
Avoid bearing failure while restarting machines after prolonged stoppage. Restarting machines without priming after prolonged stoppage can have adverse effect on the components and land you in further downtime. While there is a vast range of bearings suited for every application based on speed, load and alignment, optimal lubrication is a common yet critical requirement for efficient performance. Here is a list of possible scenarios that can adversely affect bearing performance due to lubricant starvation and remedies to ideally prep the machine before restart.

